Past events at MIOT
Fracture Treatment using Tibia Nail Advanced System for the 1st time in India
MIOT International, a renowned healthcare institution in India, is known for its dedication to embracing new innovations in orthopaedics. Since its inception, MIOT has been committed to advancing medical technology and improving patient care. With an expert team and a strong focus on innovation, MIOT consistently incorporates cutting-edge advancements in orthopaedic treatments. Continuing the path of excellence, MIOT is happy to introduce the Tibia Nail Advanced System for the 1st time in India.
In cities like Chennai, where two-wheeler traffic is heavy, large hospitals such as MIOT witness around 14 or 15 occurrences of low-velocity fractures per day. This interesting and useful approach can significantly increase the chances of success and reduces the risk of disability.
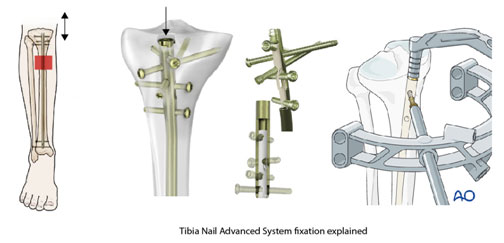
The Tibia Nail Advanced System designed by AO-Synthes, Switzerland, incorporates Angle-Stable technology which provides enhanced stability and promotes faster healing in patients with tibial fractures. The Department of Orthopaedics at MIOT developed a new nailing method to provide patients undergoing treatment for fractures near the knee joint with high levels of structural stability and a multitude of benefits.
What is Nailing Procedure?
Nailing is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a metal rod or nail through the top of the fractured bone. This rod acts like a splint inside the bone, keeping it in place. This allows for faster healing and faster return to activity compared to traditional methods like casting, internal or external fixation. This method does not disturb the biology of the bones, tissue, nerves, and major arteries that are already heavily injured and provides support and stability to the bone, allowing it to heal properly without compromising its blood supply or nutrition.
Traditional Surgery for Tibial Fractures
Traditional tibial surgery refers to any surgery done on the tibia, the larger bone in the lower leg. This type of surgery is usually done to treat different conditions and injuries in the tibia, such as fractures, deformities, infections, or tumours.
While traditional surgery can be effective in some cases, it has some drawbacks compared to the nailing method:
Invasive: Traditional surgery often requires large incisions, which can cause more damage to the surrounding tissues. This leads to more pain after the surgery, longer recovery times, and a higher risk of complications like infection and excessive bleeding.
Disruption of soft tissues: During traditional surgery, the surgeon may need to tend to the fracture by going through the already damaged muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the bone to access the affected area. This disrupts the soft tissues and can make healing take longer, increase the risk of scar tissue, and potentially result in long-term stiffness or even disability.
Higher risk of infection: Traditional surgery has a higher risk of infection because of the larger incisions and exposure of the surgical site to bacteria. Infections can prolong hospital stays, require additional surgeries, and lead to complications like bone infections.
Traditional Tibial Surgery
- The fractures that occur near proximal third of the tibial bone are hard to treat without disturbing the biology of the surrounding bones, tissues, nerves, and arteries.
- The traditional surgery uses the plating method for good stability. However, it exposes the fractured bony fragments and strips off the soft tissues, thereby causing a loss of blood supply to the bone end, which may lead to severe soft tissue healing problems.
- Operating in the zone of the injured tissues can also cause infections and delay fracture healing.
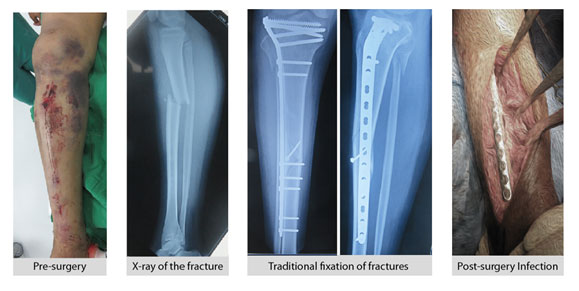
Delayed weight-bearing: After traditional surgery, patients often have to avoid putting weight on the affected leg for a longer period. This can impact mobility, independence during recovery, and potentially lead to muscle weakness and joint stiffness.
Longer hospitalization: Traditional surgery usually requires a longer hospital stay compared to less invasive procedures. These can be expensive, disrupt normal routines, and cause disability for patients.
Advantages of using Tibia Nail Advanced System Over Traditional Tibial Surgery
Enhanced stability: The special angle-stable technology used in the Tibia Nail Advanced System provides strong stability, reducing the chance of bone rotation or displacement. This stability promotes better alignment of the fractured bones and aids in the healing process.
No destruction of soft tissues: By going directly through the top of the bone into the centre of the virgin area above the kneecap, the nailing method avoids opening heavily injured or damaged wounds. This minimizes disruption to important tissues, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, reducing the likelihood of complications.
MIOT’s Tibia Nail Advanced System
- MIOT International is launching the Tibia Nail Advanced System for the 1st time in India to improve stability and healing for fractures around the knee.
- The Supra-Patellar Nailing method is a keyhole procedure that involves a small incision made at the top of the knee joint, through which a specially designed nail is inserted into the tibia bone.
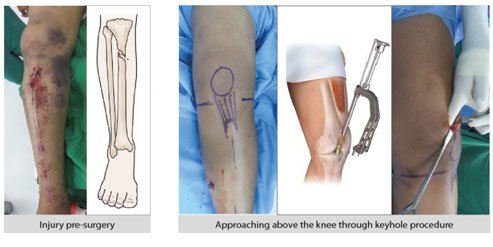
Reduced risk of infection: The nature of this nailing method lowers the risk of infection compared to traditional open surgeries. Smaller incisions and less tissue dissection minimize the exposure of the surgical site to potential pathogens.
Decreased nerve damage: The careful approach of the nailing method helps protect nerves, reducing the risk of nerve damage during the surgical procedure. This can lead to better postoperative sensory and motor function.
Preservation of blood supply: Nailing preserves the blood supply to the fractured bone since the technique does not disrupt the outer layer of the bone responsible for blood supply. Preserving the blood supply promotes faster healing and reduces the risk of complications such as non-union (failure of bone healing).
Reduced risk of malalignment: Intramedullary nails can help prevent malalignment of the fractured bone segments. The rigid nail acts as an internal splint, maintaining the alignment of the bone while healing. This can be particularly beneficial in complex fractures or cases where accurate alignment is crucial.
Early mobilization and weight-bearing: Nailing allows for early mobilization and weight-bearing compared to some other surgical techniques. The stable fixation provided by the nail allows patients to start walking and bearing weight sooner, which can lead to faster functional recovery and reduced hospital stays.
- This nail is guided down the bone to the fracture site and secured in place on both ends with angle stable, multi angle interlocking screws.
- Once the nail is in place, it acts as a stabilising device, allowing the fracture to heal without the need for a cast or external support.
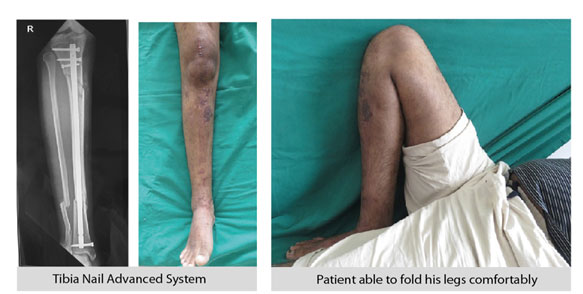
Recovery in 4 weeks
- After a 4-week follow-up of a severely injured patient, we can see that the patient has completely recovered around the ankle and knees, and is able to bend his knee, move his ankle freely.
- This technique not only minimises the damage of soft tissues but also allows the patient to bend their knees post-surgery, which is not possible with traditional casting methods.
MIOT International, the No. 1 Orthopaedic Hospital, is known for its innovative approaches to orthopaedic surgery and has been at the forefront of medical advancements for more than two decades. Patients from across the globe seek out MIOT’s expertise for complex orthopaedic procedures such as tibial fractures, joint replacements, spine surgeries, and other advanced medical treatments. In addition to its clinical expertise, MIOT is also committed to research and education, which led to the development of a new method for fracture treatment using the Tibia NailAdvanced System. This method is a breakthrough in orthopaedic surgery because it allows faster and more accurate healing of tibial fractures without disturbing the biology of the already damaged soft tissues, reducing recovery time, and therefore improving overall patient outcomes.



